Understanding the outputs
It’s easy.
The .h5 file
The main output product is a HDF5 .h5 file. This format has many viewers such as HDFView or HDFCompass and APIs such as Cpp, FORTRAN and Python.
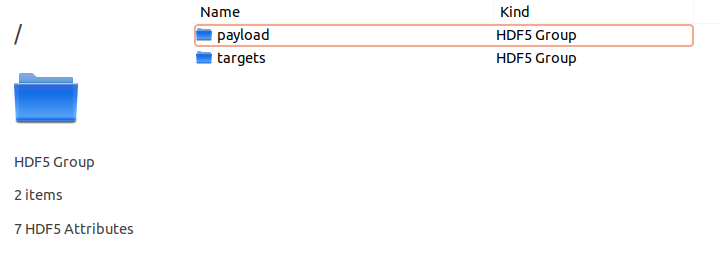
payload
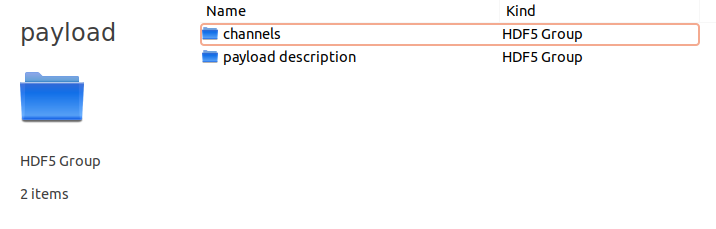
The payload group contains all the information related to the instrument. Inside you will find a group for each channel and a group called payload description containing the parsed xml payload description file.
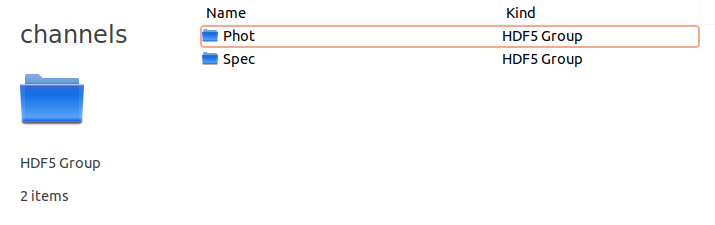
Inside the channels group you will find a group for each channel called as the channel name. In this case you have Phot and Spec as they are the channels contained in payload_example.xml.
Let’s open a channel now.
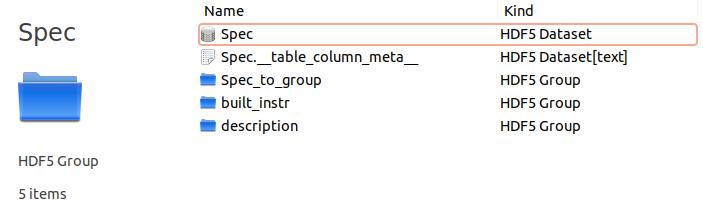
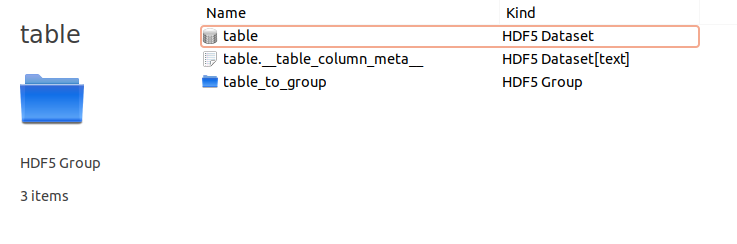
Inside each channel you find a dataset that is called as the channel. This is the main channel output table.
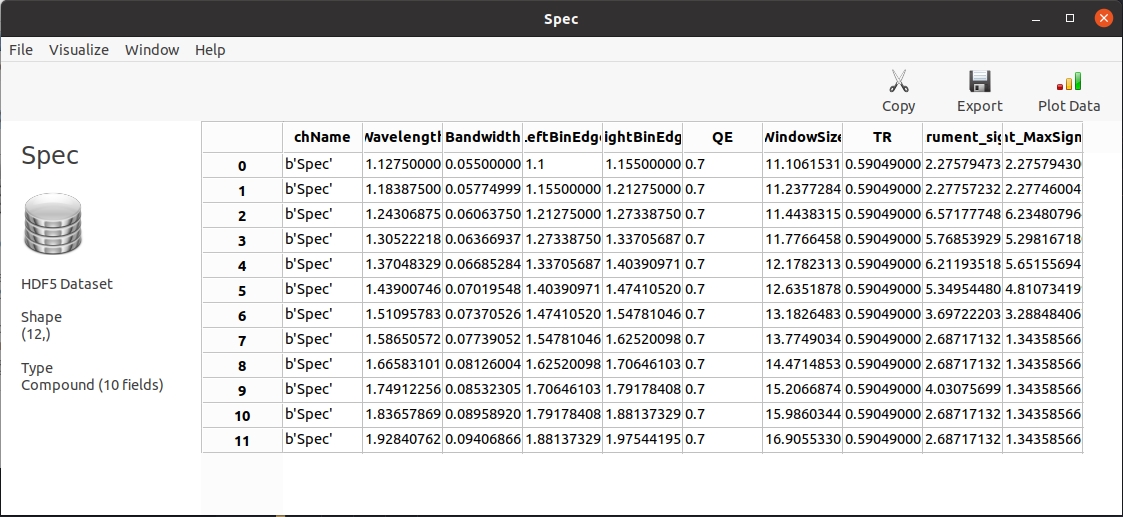
Inside the text dataset called as the channel plus _table_column_meta_ are contained the table metadata.
The couple dataset + metadata text can be read into an astropy quantity table (QTable) with the function load().
The _to_group directory contains the just described table converted into a dictionary and stored.
The description group contains the parsed section of the payload description file that contains the channel information.
Finally, the built_instr directory contains processed information related to the channel that allow ExoRad to load an already built channel without initialize again the instrument.
target
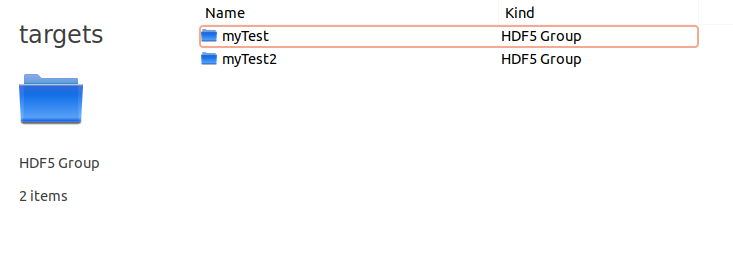
Inside the targets group you will find a directory for each target.
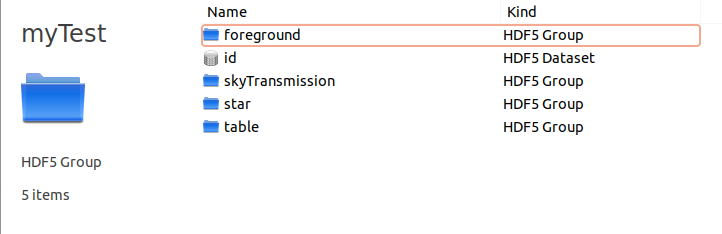
Inside each target there will be a list of subdirectories containing everything that concerns the target. For example you will find here all the information about the foregrounds and the star. skyTransmission is the total transmission resulting from all the foregrounds.
The final results are stored in the table group.